Article
Keeping up with AI lingo: 10 AI keywords to broaden your expertise
Artificial Intelligence, it’s not new anymore. However, it can be a tough nut to crack when it comes to effective usage and implementation. With new terms popping up daily, it’s easy to feel lost. Here are 10 AI concepts explained in plain language, with practical examples and strategic takeaways.
About the series
The “Keeping up with AI Lingo” series is designed to make artificial intelligence accessible to everyone. Each blog post explores different AI concepts, explained in clear language and tailored for diverse audiences, from curious beginners to seasoned professionals. Whether you’re looking to deepen your understanding or stay current with the latest trends, this series will help you confidently navigate the evolving world of AI.
Who is this article for?
This article is for anyone curious about AI. Whether you’re a student, entrepreneur, professional from any field, or simply eager to learn more. It contains 10 essential AI keywords that are important to know about. By mastering these terms, you’ll be able to participate confidently in AI-related conversations and make smarter choices in your work or daily life.
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Definition: AI’s ability to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- How it works: Breaks text into tokens, analyzes grammar, sentiment, and meaning.
- Why it matters: Enables AI tools to read, write, and respond like humans.
- Example: Summarizing thousands of customer reviews to spot sentiment trends, in any language.
- Strategic Implication: Powers content creation, social listening, and customer support at scale. Especially useful for multilingual markets like Belgium.
2. Token Context Engineering
- Definition: Structuring prompts so the most relevant info fits within a model’s token limit.
- How it works: Large Language Models (LLMs) process text as tokens. This technique prioritizes and compresses content so nothing critical gets cut off.
- Why it matters: Keeps outputs coherent, brand-aligned, and actionable.
- Example: Crafting prompts that include tone, product features, and SEO keywords, all within token limits.
- Strategic Implication: Enables scalable, brand-consistent content generation across channels.
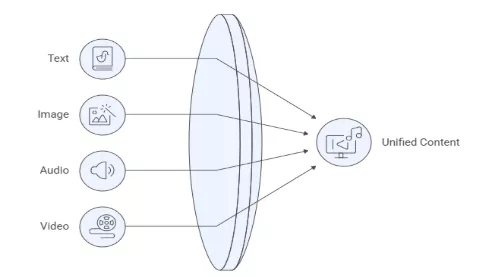
3. Multimodal Fusion Models
- Definition: AI systems that combine text, image, audio, and video inputs for unified outputs.
- How it works: Trained to interpret and generate across formats, just like humans consume content.
- Why it matters: Creates richer, more engaging campaigns.
- Example: Generating Instagram posts with captions, visuals, and hashtags in one go.
- Strategic Implication: Streamlines cross-channel creative production and improves campaign cohesion across different regions.
4. Synthetic Persona Modeling
- Definition: AI-generated customer archetypes based on behavioral and predictive data.
- How it works: Builds synthetic profiles to simulate how different personas might respond.
- Why it matters: Lets marketers test ideas without slow A/B testing or real-world risk.
- Example: Testing a loyalty program across synthetic personas representing Flemish, Walloon and Brussels-based shoppers.
- Strategic Implication: Accelerates innovation and reduces campaign risk.
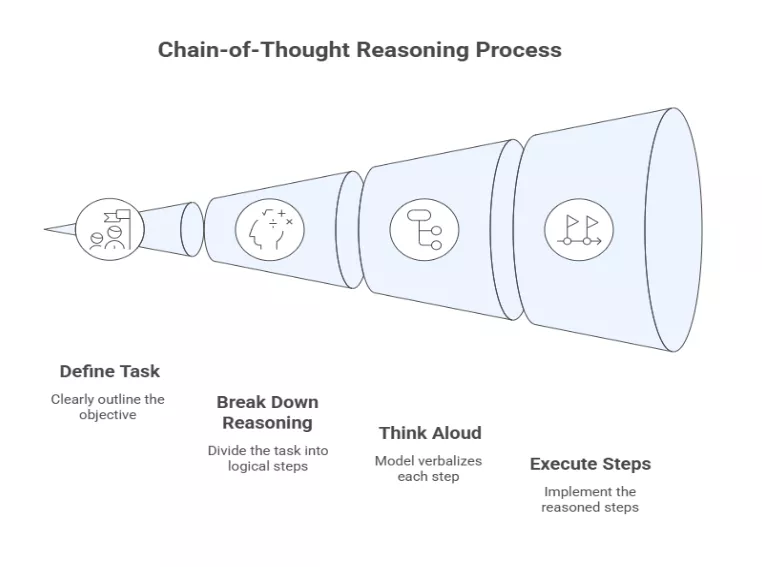
5. Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
- Definition: A prompting method that guides AI through step-by-step logic.
- How it works: Instead of jumping to an answer, the model “thinks aloud,” breaking down reasoning.
- Why it matters: Improves accuracy and transparency for complex tasks.
- Example: Building a campaign plan by reasoning through audience, channels, and KPIs.
- Strategic Implication: Turns AI into a strategic partner, not just a content generator.
6. AI Governance Frameworks
- Definition: Policies and tools for managing ethical, legal, and operational risks in AI.
- How it works: Includes bias audits, transparency protocols, and performance monitoring.
- Why it matters: Builds trust and ensures compliance with brand values and regulations.
- Example: Monitoring AI-generated content for bias and tone via a governance dashboard.
- Strategic Implication: Future-proofs AI investments and ensures compliance with Belgian and EU regulations.
7. Federated Prompting
- Definition: Distributed prompting across multiple models or data silos without centralizing sensitive data.
- How it works: Prompts run locally, results aggregate. No raw data moves.
- Why it matters: Preserves privacy and meets data regulations while enabling personalization.
- Example: Generating localized content for global markets without sharing customer data across borders.
- Strategic Implication: Enables compliant, scalable AI adoption worldwide.
8. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Definition: Combines generative AI with real-time data retrieval for grounded outputs.
- How it works: Pulls relevant documents before generating a response.
- Why it matters: Reduces hallucinations and ensures accuracy.
- Example: A chatbot fetching live product specs before answering questions.
- Strategic Implication: Enhances trust and utility in customer-facing applications.
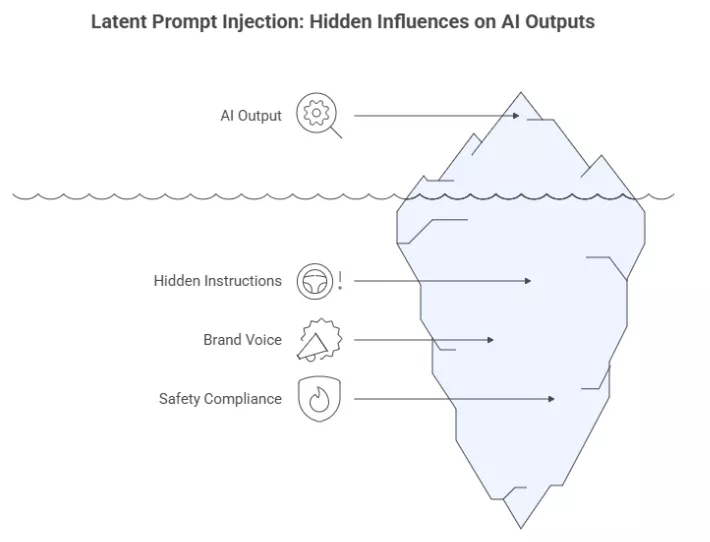
9. Latent Prompt Injection
- Definition: Embedding hidden instructions in prompts to subtly influence AI outputs.
- How it works: Invisible cues steer tone, structure, or compliance without cluttering prompts.
- Why it matters: Maintains brand voice and safety in automated workflows.
- Example: Ensuring every AI-generated post includes a CTA and seasonal messaging.
- Strategic Implication: Keeps automation aligned with brand standards.
10. Semantic Embedding Spaces
- Definition: High-dimensional representations of meaning that help AI understand relationships.
- How it works: Converts text, images, or behaviors into vectors that capture semantic similarity.
- Why it matters: Goes beyond keywords to grasp context, tone, and intent.
- Example: Clustering customer feedback in Dutch & French to spot emerging needs in the Belgian market.
- Strategic Implication: Enables deeper segmentation and predictive insights for campaign design.
Tip for managers and decision makers: These concepts aren’t just technical jargon, they’re strategic levers. Understanding them helps you ask better questions, set smarter KPIs, and future-proof your marketing stack.
Need support? We provide support for every stage of your AI transformation journey. Whether you’re exploring your first use case or scaling your AI marketing strategy, we are here to guide you every step of the way.
Schedule a no-obligation 30 minute call here with one of our experts to see how we can help!
